Understanding business transactions can sometimes feel like learning a new language, particularly when it comes to payment terms. One term you’ll often come across is “Net 30,” a common practice that can greatly affect your cash flow and business relationships.
Whether you’re an experienced business owner or just beginning your business journey, knowing the details of Net 30 is essential for smooth and successful transactions. In this detailed guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about Net 30 payment terms, from what it means and its advantages to possible issues and real-life examples.
So, grab a cup of coffee, get comfortable, and let’s clear up the mystery of Net 30 together!
Understanding Net 30 Payment Terms
Hi everyone! Whether you’re an experienced business owner or just beginning your entrepreneurial path, knowing about payment terms is really important for making things go smoothly and successfully. One of the most common terms you’ll see is “Net 30.” At first, it might look simple, but there are some details and effects that are important to understand. So, let’s get into the details of Net 30 and learn everything you need to know!
Definition and Explanation of Net 30 Terms
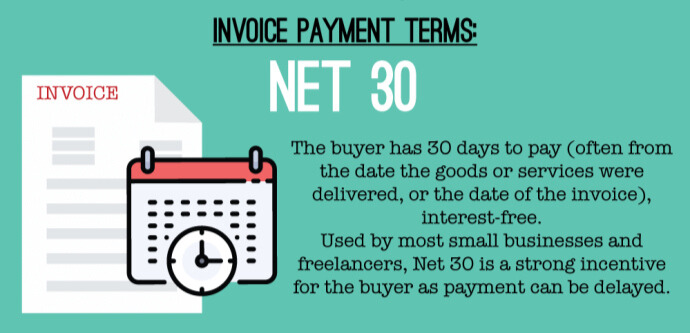
At its core, “Net 30” is a type of credit that lets the buyer pay for goods or services within 30 days after getting the bill. This means the buyer gets the goods or services first and then has 30 days to pay the seller.
Imagine you’re a small business owner who just got a shipment of goods. With Net 30 terms, you can sell some of those goods before you have to pay your supplier. This can be a big help for managing your money, especially if you don’t have a lot of cash on hand.
Key things to remember about Net 30:
- All days count: The 30-day period includes Saturdays, Sundays, and holidays.
- Begins with the invoice date: The 30 days start from the date on the invoice, not the date the items were delivered or the services were provided.
- Clear invoices are important: A good invoice should clearly show the Net 30 terms, the invoice date, the total amount to be paid, and any other important payment details.
How Net 30 Differs from Other Payment Terms?
Net 30 is only one part of the payment terms you need to know. There are many other terms used in business, each affecting both buyers and sellers in different ways. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common ones:
- Payment in Advance (PIA): This is the best option for sellers because it means they get paid before they send any products or provide any services. It lowers the risk for the seller, but it might not be as good for buyers, especially when dealing with new or unfamiliar suppliers.
- Net 15: This is a shorter payment period than Net 30, meaning buyers have to pay within 15 days of getting the invoice. This helps sellers keep their cash flow strong, but it gives buyers less time to handle their money.
- Net 45/60/90: These longer payment periods give buyers more time to make money or collect payments from their own customers. However, this can be tricky for sellers because it affects their cash flow and planning.
- End of Month (EOM): Payment is due at the end of the month when the invoice is sent. This makes accounting easier for both buyers and sellers because payments fit into monthly routines.
- 2/10 Net 30: This offers a discount (usually 2%) if the buyer pays within 10 days, with the full amount due within 30 days. It incentivizes early payment while still providing the standard 30-day credit period.
Knowing the distinctions between these payment terms allows you to negotiate better and select the choices that most fit your business requirements.
How Net 30 Works for Invoicing

Now that we know what Net 30 means, let’s see how it works in real situations involving invoices. Creating clear and accurate invoices is crucial for maintaining good business relationships and ensuring timely payments.
The Process of Invoicing with Net 30 Terms
Using Net 30 terms for invoicing is quite simple. Here’s a detailed guide on how to do it:
- Clearly Show the Terms: When making your invoice, make sure “Net 30” is clearly written in the payment terms area. This makes it clear when payment is due.
- Include All Important Details: A complete invoice should have:
-
- Invoice Number: A special number to help track the invoice.
- Invoice Date: The date the invoice was made, which starts the 30-day payment period.
- Description of Goods/Services: Explain exactly what was given to the buyer.
- Quantities and Prices: List how many items or services were provided and their cost.
- Total Amount: Add up the total cost, including any taxes or discounts.
- Payment Instructions: Give clear directions on how the buyer can pay (e.g., bank details, online payment link).
- Deliver the Invoice Promptly: Send the invoice to the buyer as soon as the goods or services are delivered or rendered. This starts the 30-day payment clock.
- Maintain Records: Keep a copy of the invoice for your own records and track when payment is received.
Try using invoicing software to make the process easier and reduce mistakes. Many software choices have templates and features that help you create professional invoices with Net 30 terms quickly.
Benefits for Both Buyers and Sellers
Net 30 terms offer advantages for both sides of the transaction:
Benefits for Buyers:
- Better Cash Management: Buyers have more time to handle their money and possibly make money from the products or services before they need to pay.
- Payment Flexibility: The 30-day window allows buyers to match their payments with other financial needs.
- Credit Building: Regularly paying on time with Net 30 terms can help create a good credit record.
Benefits for Sellers:
- Higher Sales: Giving customers 30 days to pay can make your business more appealing, which might lead to more sales.
- Better Competitiveness: In fields where 30-day payment terms are typical, offering this can help your business stay ahead of the competition.
- Easier Bookkeeping: With a set payment date, it’s simpler to keep track of money coming in and plan for future income.
However, it’s crucial to consider both the advantages and the risks. For customers, late payments can hurt their credit and result in extra fees. For sellers, allowing customers to pay later carries the risk of not getting paid on time or at all, which can affect cash flow.
Why Use Net 30 for Invoicing?

We’ve explained what Net 30 is and how it operates, but you might still be asking: “Why should I use it?” There are several strong reasons why Net 30 has become a common payment method in many fields. Let’s look at the benefits and possible issues to help you decide if it’s suitable for your business.
Advantages of Offering Net 30 Terms
For Sellers:
- Increase Sales and Draw in Customers: In a competitive market, offering flexible payment options like Net 30 can make your business stand out. This can attract new customers, especially smaller companies or startups, who value the extra time to manage their money.
- Strengthen Customer Connections: Giving credit to your customers shows trust and friendliness. This can create loyalty and encourage them to keep doing business with you.
- Better Cash Flow Management: Even though it might seem strange, offering Net 30 can actually help you predict your cash flow more accurately. With clear payment dates, you can better estimate when you’ll get paid and manage your finances accordingly.
- Cut Down on Collection Work: When payment expectations are clear from the start, it can reduce the need for frequent reminders and collection efforts.
For Buyers:
- Improved Financial Freedom: Net 30 helps you manage your money better by giving you extra time. You can use this time to make more money, get paid by your own customers, or take care of other financial needs.
- Better Inventory Control: If you buy items to sell, Net 30 lets you sell some of those items before you have to pay for them, which helps your money flow better.
- Stronger Supplier Connections: By always paying your suppliers on time with Net 30, you build trust and show them you are reliable.
Potential Challenges of Using Net 30
While Net 30 offers numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of the potential challenges:
For Sellers:
- Late Payments: When you offer credit, there’s always a chance that customers might pay late. This can mess up your cash flow and make it hard to pay your own bills.
- More Complicated Accounting: Dealing with invoices that have different payment deadlines can make your accounting work more difficult.
- Risk of Unpaid Debts: Sometimes, businesses may not pay you back, which can result in you losing money.
For Buyers:
- Temptation to Spend Too Much: Having access to credit can sometimes cause you to spend more than you can afford, leading to more debt than you can handle.
- Risk of Late Payment Fees: Missing the 30-day deadline can result in extra fees or harm your credit score.
Mitigating the Challenges:
- Credit Checks: Sellers can evaluate new customers’ ability to pay by checking their credit. This helps lower the chance of not getting paid.
- Clear Communication: Keeping in touch with customers or suppliers about when payments are expected can prevent confusion and late payments.
- Automated Reminders: Use invoicing tools to automatically send payment reminders before the due date.
- Early Payment Discounts: Offer discounts for paying early to encourage quicker payments and improve your cash flow.
By understanding the pros and cons and using strategies to handle risks, you can effectively use Net 30 terms to help your business.
Examples of Net 30 Transactions in Invoicing
Okay, let’s make Net 30 more clear with some practical examples! Looking at how these payment terms work in various situations can help you understand them better and see how they could be used in your own business.
Real-World Scenarios of Net 30 Usage
- Scenario 1: The Wholesaler and the Retailer: Picture a wholesaler selling clothes to a store. The wholesaler sends an invoice with Net 30 terms. This means the store can get the clothes, put them on the shelves, and try to sell them before they have to pay. This is a common way Net 30 helps make supply chain transactions go smoothly.
- Scenario 2: The Freelancer and the Client: A freelance graphic designer finishes a logo project for a client. They send an invoice with Net 30 terms. This lets the client look at the work, use the logo in their materials, and maybe see some early benefits before they need to pay.
- Scenario 3: The Manufacturer and the Distributor: An electronics company sells a group of tablets to a distributor. The company gives the distributor 30 days to pay on their bill, allowing the distributor to find stores to sell the tablets and maybe even sell some before they have to pay the company.
These are just a few examples, and there are many more ways to use it! The main point is that Net 30 offers a flexible way for businesses to handle their money and keep good relationships with their customers or suppliers.
Different Industries Where Net 30 is Common
Net 30 payment terms are used in many different industries. Here are some examples where they are commonly found:
- Wholesale and Distribution: Net 30 is often used in deals between wholesalers, distributors, and retailers.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers usually give their customers 30 days to pay, which helps them make bigger orders and keeps the business relationship strong.
- Business-to-Business (B2B) Services: Many B2B service providers, like marketing agencies, IT consultants, and accounting firms, use Net 30 terms.
- Construction and Building Materials: In the construction industry, Net 30 is commonly used for buying building materials, renting equipment, and paying subcontractors.
Although these are some of the most common fields, you might also come across Net 30 in other areas. It’s always helpful to learn about the typical payment methods in your particular industry.
And that’s it! We’ve finished our detailed guide to understanding Net 30 payment terms. I hope this information was useful and that you now feel comfortable dealing with Net 30 invoicing. Keep in mind that clear communication, prompt payments, and a good grasp of payment terms are crucial for successful business dealings.
Conclusion
Here it is! We’ve gone through the details of Net 30 payment terms, looking at what it means, its advantages, possible issues, and how it’s used in real life. Hopefully, you now feel ready to handle this common invoicing method with confidence.
Remember, good communication, making payments on time, and understanding payment terms well are important for strong business relationships and keeping a healthy cash flow. Whether you’re buying or selling, Net 30 can be a useful tool when used wisely and responsibly.
As you keep working on your business, keep learning, keep improving, and don’t be afraid to ask for explanations when you come across new or unfamiliar payment terms. The business world is always changing, and staying informed is crucial for success.
Good luck on your business journey!








